Query Processing
Once an index is built, we need to process the data in it to produce query results.
Two simplest two query processing techniques:
- Document-at-a-time
- Term-at-a-time
Document-at-a-time Query Evaluation
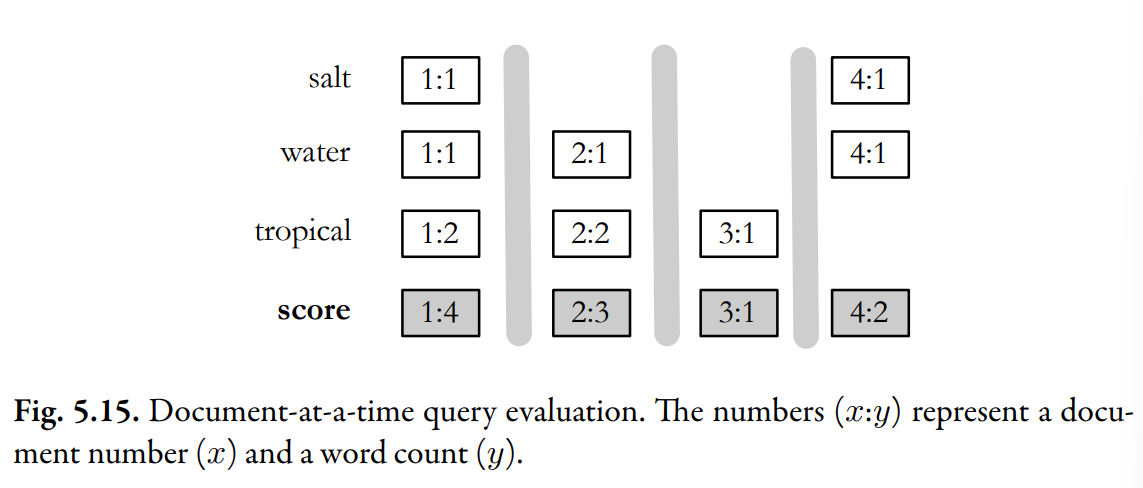
Above picture shows document-at-a-time retrieval for the query "salt water tropical".
The inverted lists are shown horizontally, and the postings have been aligned so that each column represents a different document. The inverted lists in this example hold word counts, and the score which is the sum of the word counts in each document.
The vertical gray lines indicate the different steps of retrieval. In this first step, all the counts for the first document are added to produce the score for that document. Once the scoring for the first document has completed, the rest of the documents will then be processed one by one.

Benefit
The primary benefit of this method is its frugal use of memory. The only major use of memory comes from the priority queue, which only needs to store entries at a time.
Term-at-a-time Query Evaluation
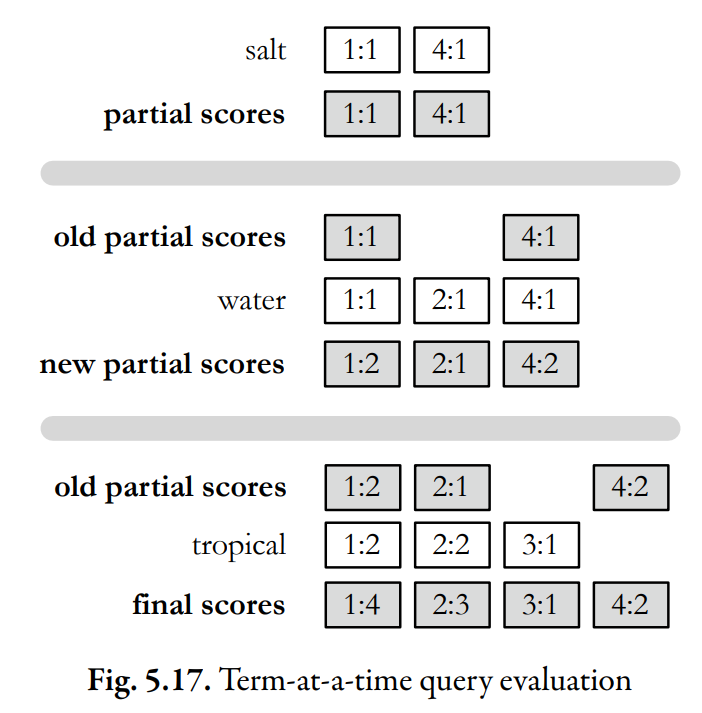
The gray lines indicate the boundaries between each step.
Disadvantage
The primary disadvantage of the term-at-a-time algorithm is the memory usage required by the accumulator.
Optimization Techniques
Two main classes of optimization for query processing.
- Read less data from the index.
- Process fewer documents.