Voltage
Objectives:
- Identify the six most common voltage sources.
- Describe six different methods of producing electricity.
- Define a cell and a battery.
- Describe the difference between primary and secondary cells.
- Describe how cells and batteries are rated.
- Identify ways to connect cells or batteries to increase current or voltage output or both.
- Define voltage rise and voltage drop.
- Identify the two types of grounds associated with electrical circuits.
Voltage Sources
- Friction
- Magnetism
- Chemicals
- Light
- Heat
- Pressure
Friction
The triboelectric effect is the phenomenon where certain materials become electrically charged after they come into frictional contact with a different material.
How it works step by step:
- Contact - When two different materials touch, some electrons may be transferred from one material to the other.
- Separation - When the materials are pulled apart, one material ends up with extra electrons (negatively charged), and the other ends up with too few electrons (positively charged).
- Static charge - This difference in charge creates static electricity, which can remain until the charges either discharge or slowly leak away.
note
Rubbing a balloon on your hair.
- Hair loses electrons and becomes positively charged.
- the balloon gains the electrons and becomes negatively charged.
- When you bring the negatively charged balloon close to the wall, the negative charges on the balloon repel the free-moving electrons on the surface of the wall.
- The side of the wall closest to the balloon is now left with a slight excess of positively charged protons. Even though the wall as a whole is still neutral.
- Finally, the negatively charged ballon is now attracted to the newly created positively charged surface on the wall.
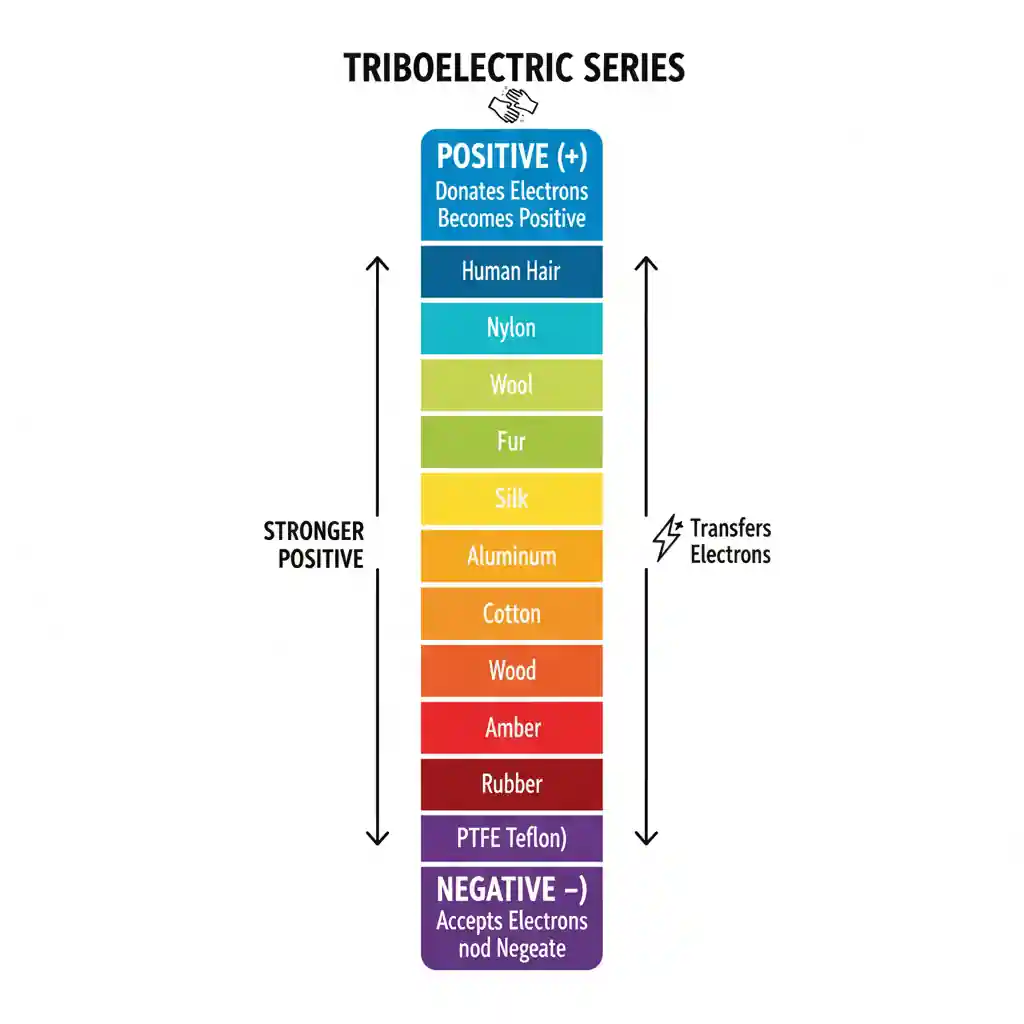
Triboelectric Series
- Some materials "like" to give away electrons (becoming positive).
- Others "like" to take electrons (becoming negative).
Triboelectric series is a list of materials ranked by their tendency to gain or lose electrons.
Magnetism
- The most common method of producing electrical energy.
- Produced using generator powered by steam from nuclear power or coal, water, wind, or gasoline...
Chemical
- The second most popular method of producing electrical energy.
Light
- Photovoltaic cell
- A single cell can produce a small voltage.
- Many cells must be linked to produce a usable voltage and current.